Describe the Potential Costs of Both Scarcity and Choice
A choice is the decision made from the opportunities presented. Describe how monasticism developed during the Middle Ages.

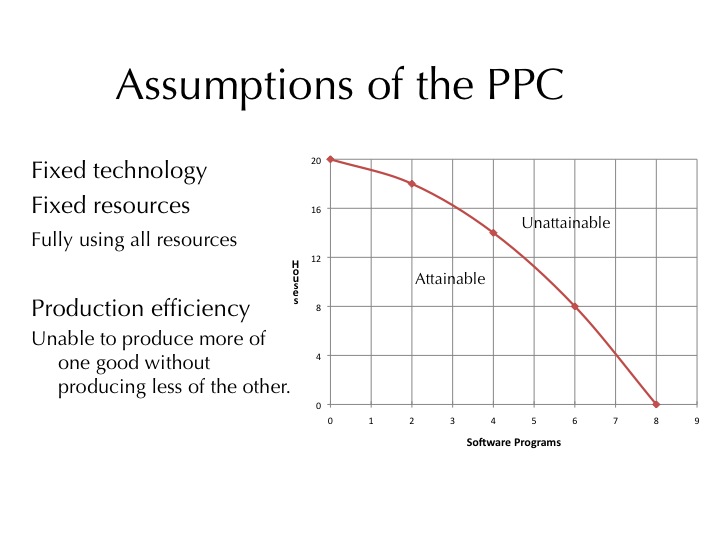
2 The Economic Problem Scarcity And Choice Chapter Outline Ppt Video Online Download
Cost of the trip home D.

. Materials Needed Student Journal pages 5-1 and 5-2 Activity 3 one copy for each student. 15 The Production Possibility Frontier Point C is one of the possible. Time spent at home B.
Scarcity and Choice 1. These three concepts scarcity choice and opportunity cost help form the foundation for economic thinking and reasoning. Again notice the common theme of the necessity of choice and its consequences running throughout all of these definitions.
An opportunity cost equals the value of the next-best foregone alternative whenever a choice is made. When there is scarcity and choice there are costs. Scarcity choice and opportunity costs.
After reading this article you will learn about. Opportunity Cost Scarcity Capital Goods Choice Consumer Goods Communism Content Standards and Benchmarks 1 3 and 15. Scarcity means we have to decide how and what to produce from these limited resources.
Scarcity as a Mindset. They imply each other and. Describe two different types of resources.
Resources are anything provided by nature or previous generations that can be used directly or indirectly to satisfy human wants. What is mechanical energy used to describe. As a result they must choose some things and give up others.
Published by James Taylor. Scarcity Choice and Opportunity Cost. Human wants are unlimited.
The opportunity cost of an action is what you must give up when you make that choice. None of the above Riding your bicycle 20 miles every day. Why Having Too Little Means So Much changed the nature of the discussion about scarcity by suggesting that scarcity of a wide variety of resources eg both.
25 June 2019 by Tejvan Pettinger. Opportunity cost is the benefit of the next best alternative sacrificed due to the current choice. Answer 1 of 6.
All of the above E. Problems of calculating opportunity cost. This applies equally to the poor and the rich people.
We live in a world of scarcity. Describe the potential costs of both scarcity and choice. Yields more of both goods but it is not attainable given the amount of resources available in the economy.
Up to 24 cash back find examples of scarcity and choice. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. For each of the following describe some of the potential opportunity costs.
An introduction to the concepts of scarcity choice and opportunity cost. Scarcity in economic terms means that resources are limited and cannot satisfy all the human wants. It means there is a constant opportunity cost involved in making economic decisions.
It is the value of the next best opportunity. Opportunity cost is a direct implication of scarcity. Another way to say this is.
Four factors of production. Every choice is accompanied by opportunity cost. If there is no scarcity there is no choice and no opportunity cost ie free goods.
Understand opportunity cost as the cost of making a choice. Economists are careful to consider all of the costs of making a. The Problem of Scarcity 2.
Whenever a choice is made something is. The production possibilities frontier is used to illustrate the economic circumstances of scarcity choice and opportunity cost. Both potential and kinetic energy.
Scarcity refers to resources being finite and limited. The basic economic problem is scarcity that is we have limited resources and our wants are unlimitedtherefore we have to make a choice since we cannot produce everything because of lack of resources and this involves an opportunity costsince if we want to produce good x we have to forego or sacrifice good y. Choice means selection of something for consumption or production.
Time spent studying This is the correct answerC. Economic Choice and Opportunity Cost Objectives Students will recognize the need to make economic choices. Concepts of Scarcity And Choice - Economics Notes Concepts of ScarcityScarcity refers to the condition of insufficiency where human beings are incapable to fulfill their wants in a sufficient manner.
1 requires time and information limitedmisinformation at time of decision time needed to gather information on alternatives 2 vary with circumstance different situation different alternatives Rational Decision. Scarcity Choice and Opportunity Cost. The Problem of Choice.
Economics is sometimes called the study of scarcity because economic activity would not exist if scarcity did not force people to make choices. To describe the concept of the production possibilities frontier assume that we live on an island that has only two cities Lake and Desert and two industries cars and airplanes. Opportunity Cost This concept of scarcity leads to the idea of opportunity cost.
Scarcity The study of economics begins with the concept of scarcity. Check all that apply. In other words it is a situation of fewer resources in comparison to unlimited human wants.
Understand that scarcity makes economic choices necessary. Scarcity is one of the fundamental issues in economics. The ability to produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than another producer.
Based on the concept of opportunity cost. Productive resources are limited. Using examples explain why people cannot have everything they want scarcity and describe how people respond choice.
The cost of any choice is the option or options that a person gives up. Cost of maintaining the. Therefore people cannot have all the goods and services they want.
When a choice is made the other best alternative foregone becomes the opportunity cost. In contrast to earlier work on scarcity that focused on differences in the experiences of impoverished versus middle-class consumers Mullainathan and Shafirs book Scarcity. Going home for Thanksgiving vacation.
Where there is scarcity there is choice and every choice has its opportunity cost. In this article we will discuss about Scarcity and Choice as Economic Problems. Scarcity describes the condition in which our wants are greater than the resources available to satisfy those wants.
Capital resources include machinery equipment and structures used to produce other goods and services. Integrated GLCEs RNT0203 Identify and describe characters actions and motivations setting time and place problemsolution and sequence of events. Can you compare the relationship between scarcity and the need for choices.
Content Expectations 1 - E103. Describe the potential costs of both scarcity and choice. The Problem of Scarcity.
People want and need variety of goods and services.
/dotdash_Final_Production_Possibility_Frontier_PPF_Apr_2020-01-b1778ce20e204b20bf6b9cf2a437c42e.jpg)
Production Possibility Frontier Ppf Definition
The Production Possibility Curve The Central Economic Problem

2 The Economic Problem Scarcity And Choice Chapter Outline Ppt Video Online Download
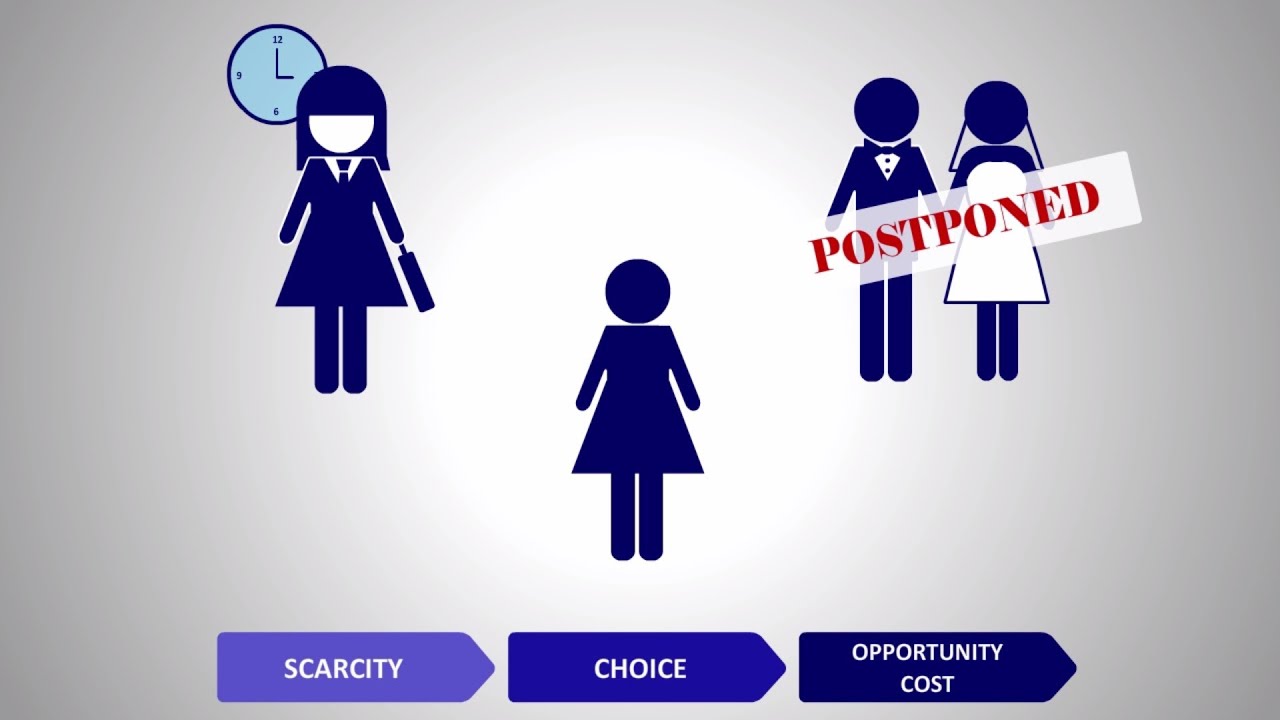
What Is The Relationship Between Scarcity Choice And Opportunity Cost Lisbdnet Com
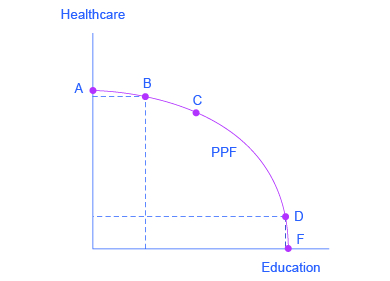
The Production Possibilities Frontier Article Khan Academy

What Is The Relationship Between Scarcity Choice And Opportunity Cost Lisbdnet Com
Ib Economics Scarcity And Choice Ib Economics

What Is The Production Possibilities Curve In Economics

The Economic Problem Scarcity And Choice Ppt Video Online Download
Chapter 2 Production Possibilities

Scarcity Trade Offs And Cost Benefit Analysis Youtube

Opportunity Cost The Production Possibilities Curve Ppc Article Khan Academy

Individual Decision Making Boundless Economics
The Production Possibility Curve The Central Economic Problem
The Production Possibility Curve The Central Economic Problem

1 The Economic Problem Scarcity And Choice Chapter Ppt Download
Comments
Post a Comment